Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are three popular terms that often create confusion. Many people use them interchangeably, but they actually refer to different levels of technology, each with a unique purpose, method, and complexity.
If you’re just starting your journey in data science or computing, understanding the differences between AI, ML, and DL is essential. This guide will explain everything clearly—even if you’re a complete beginner.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is the broadest field among the three. It refers to the science of making machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
AI focuses on enabling machines to:
- reason
- solve problems
- understand language
- perceive the environment
- make decisions
AI does not always involve learning from data. It can include rule-based systems, expert systems, and logical programming.
Examples of AI
- Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa
- Chatbots
- Rule-based fraud detection systems
- Path-planning in robotics
- Game-playing algorithms (Chess, Go)
AI is the overarching concept, under which both ML and DL exist.
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI. It focuses on enabling machines to learn patterns from data and improve automatically through experience.
Machine Learning = Systems that learn from data
Instead of manually programming rules, ML models:
- Receive data
- Find patterns
- Make predictions or decisions
Examples of Machine Learning
- Spam email detection
- Product recommendations
- Credit risk scoring
- Predicting housing prices
- Medical diagnosis based on symptoms
ML bridges the gap between traditional rule-based AI and advanced deep learning systems.
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses Artificial Neural Networks with many layers—known as deep neural networks.
Deep Learning = Machine Learning using multi-layer neural networks
DL is extremely powerful for tasks involving:
- images
- audio
- natural language
- video
- unstructured data
Examples of Deep Learning
- Face recognition on smartphones
- Self-driving car vision systems
- ChatGPT and other large language models
- Real-time language translation
- Advanced medical image analysis
Deep Learning represents the most advanced and resource-intensive branch of ML.
Visual Summary: AI → ML → DL
You can think of the relationship as nested layers:
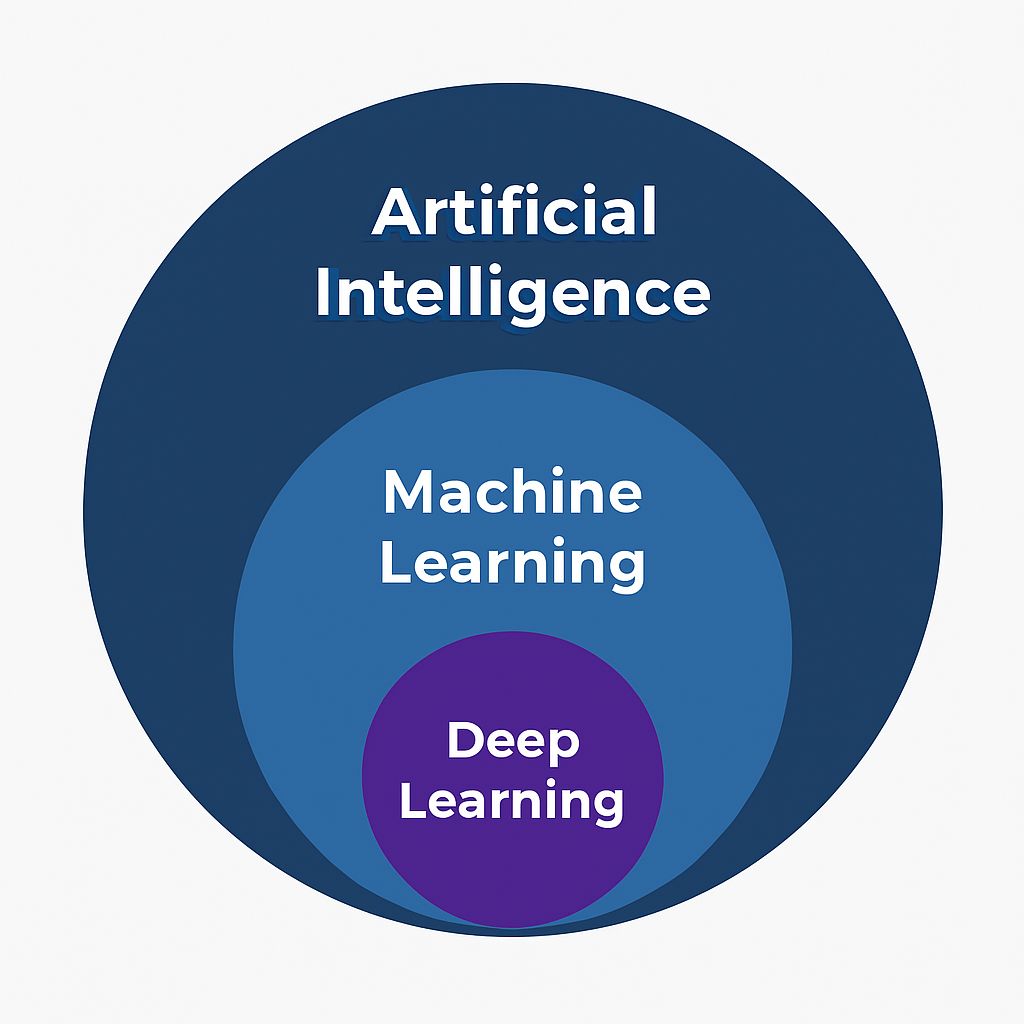
This means:
- All Deep Learning is Machine Learning
- Not all Machine Learning is Deep Learning
- All Machine Learning is part of AI
- AI is broader than both ML and DL
Key Differences Between AI, ML, and DL
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Making machines intelligent | Learning patterns from data | Using neural networks to learn from large data |
| Approach | Rules, logic, learning | Statistical learning | Neural networks |
| Data Needs | Moderate | Large datasets | Very large datasets |
| Hardware | CPU | CPU or GPU | Requires GPU/TPU |
| Complexity | Broad and varied | Moderate | High |
| Examples | Chatbots, expert systems | Spam filter, predictions | Face recognition, LLMs |
When Should You Use AI, ML, or Deep Learning?
Use AI when:
- The system requires rule-based automation
- Decision-making involves logic, rules, and data
- Tasks don’t require complex pattern recognition
Use Machine Learning when:
- You have a structured dataset
- You want to predict outcomes or classify objects
- The problem can be solved with statistical modeling
Use Deep Learning when:
- You have millions of data samples
- The problem involves images, audio, video, or text
- Maximum accuracy is required
- You can use GPUs or cloud computing
Common Misconceptions
| Misconception | Explanation (Correct Understanding) |
|---|---|
| “AI, ML, and DL are the same thing.” | They are related but not identical. ML is a subset of AI, and DL is a subset of ML. |
| “Deep Learning is always better.” | Not true. Deep Learning requires very large datasets and heavy computation. In many cases, simpler ML algorithms perform better. |
| “AI always uses neural networks.” | Incorrect. AI also includes rule-based systems, planning algorithms, and symbolic reasoning—not just neural networks. |
Conclusion
Understanding how AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning relate to each other is crucial for anyone entering the world of data science or modern computing.
Here’s a quick recap:
- AI is the overall discipline of making machines intelligent.
- Machine Learning is an AI technique that allows machines to learn from data.
- Deep Learning is a powerful form of Machine Learning that uses deep neural networks.
In the next phase of your learning journey, you’ll dive deeper into practical tools and real coding.

